Kicking off with How to Start Investing, this guide will show you the ropes on making your money work for you like a boss. From understanding the basics to diving into the investment world, get ready to level up your financial game.
Introduction to Investing
Investing is the act of allocating money with the expectation of generating income or profit in the future. It is essential for financial growth as it allows individuals to grow their wealth over time by putting their money to work. Unlike saving, which involves storing money in a safe place, investing involves taking calculated risks to potentially earn higher returns.
Benefits of Investing
Investing offers numerous benefits, including:
- Building Wealth: By investing in assets such as stocks, bonds, or real estate, individuals have the opportunity to increase their net worth over time.
- Achieving Financial Goals: Investing can help individuals reach their financial goals, whether it’s saving for retirement, buying a home, or funding a child’s education.
- Beating Inflation: Investing in assets that outpace inflation can help preserve the purchasing power of money over time.
- Generating Passive Income: Certain investments, such as dividend-paying stocks or rental properties, can provide a steady stream of income without active involvement.
Types of Investments
Investing is a key way to grow your wealth over time, but it’s important to understand the different types of investments available and the risks associated with each.
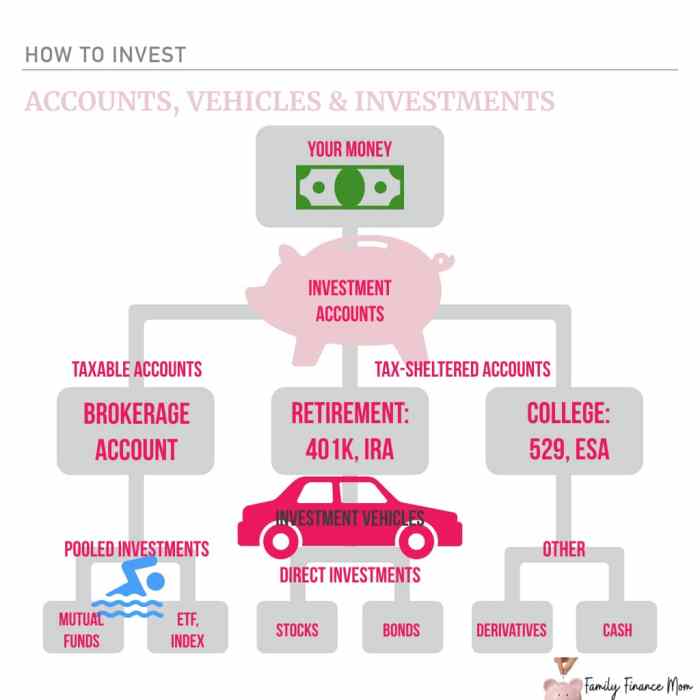
Stocks
Stocks represent ownership in a company and can offer high returns, but they also come with a high level of risk. Prices can be volatile and influenced by various factors like company performance, market conditions, and economic trends.
Bonds
Bonds are debt securities issued by governments or corporations. They are considered safer than stocks but generally offer lower returns. Bond prices are affected by interest rates and credit ratings.
Mutual Funds
Mutual funds pool money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities. They offer instant diversification but come with management fees.
Real Estate
Investing in real estate involves purchasing properties with the goal of generating rental income or capital appreciation. Real estate can provide steady cash flow but requires active management and carries risks like property market fluctuations.
Short-term vs. Long-term Investments
Short-term investments are typically held for a year or less and are more liquid, such as savings accounts or certificates of deposit. Long-term investments, like retirement accounts or stocks, are held for an extended period to benefit from compounding returns.
Setting Investment Goals: How To Start Investing
Setting clear investment goals is crucial for any investor as it provides direction and purpose to their investment journey. Without clear goals, investors may find themselves aimlessly making decisions that do not align with their long-term objectives. By defining specific investment goals, investors can create a roadmap that guides their financial decisions and helps them stay focused on achieving their desired outcomes.
Common Investment Goals
- Retirement Planning: One of the most common investment goals is to save for retirement. This involves building a portfolio that will provide a source of income during retirement years.
- Saving for Education: Another common goal is to save for education expenses, whether for oneself, a child, or a family member. Investing early can help grow funds for future educational needs.
- Buying a House: Many investors aim to invest in real estate to save for a down payment on a house or to generate rental income. Real estate can be a long-term investment strategy for achieving homeownership.
Aligning Goals with Risk Tolerance and Time Horizon
It is essential to align investment goals with risk tolerance and time horizon to ensure that the investment strategy is suitable for the investor’s financial situation and preferences.
Risk tolerance refers to the investor’s comfort level with fluctuations in the value of their investments. Investors with a higher risk tolerance may choose more aggressive investment options, while those with lower risk tolerance may opt for more conservative investments.
Time horizon refers to the length of time the investor plans to hold the investment before needing to access the funds. Longer time horizons may allow for more aggressive investment strategies, while shorter time horizons may require more conservative approaches to protect capital.
Creating an Investment Strategy

Creating an investment strategy is crucial for achieving your financial goals and securing your future. It involves carefully planning how you will allocate your funds to different investment options based on your risk tolerance, financial situation, and goals.
Asset Allocation and Diversification
Asset allocation refers to dividing your investment portfolio among different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate. Diversification, on the other hand, involves spreading your investments within each asset class to reduce risk. A well-rounded investment portfolio should have a mix of assets to balance risk and return.
- Allocate your funds based on your risk tolerance and investment goals.
- Diversify your investments to reduce risk and maximize returns.
- Regularly review and adjust your asset allocation to stay aligned with your goals.
“Don’t put all your eggs in one basket. Diversification is key to managing risk in your investment portfolio.”
Monitoring and Adjusting
Monitoring your investments is essential to ensure they are performing as expected and staying aligned with your goals. Regularly review your portfolio, track performance, and make adjustments when necessary. Consider factors such as market conditions, economic outlook, and changes in your financial situation.
- Set specific time intervals to review your investments (e.g., quarterly, annually).
- Compare your portfolio performance against benchmarks to evaluate performance.
- Rebalance your portfolio periodically to maintain your desired asset allocation.
How to Start Investing
Investing can seem overwhelming, especially for beginners, but with the right approach, anyone can start building their financial future through investments. It’s essential to take the time to research and understand the basics before diving in. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to start investing:
Step 1: Set Clear Financial Goals
- Before you start investing, determine your financial goals. Whether you are saving for retirement, a new home, or your child’s education, having clear goals will help you make informed investment decisions.
Step 2: Educate Yourself
- Take the time to educate yourself about different investment options, risk tolerance, and market trends. Understanding the basics of investing will help you make better choices and minimize potential losses.
Step 3: Start Small
- Start with small investments to gain experience and confidence. You can begin with low-cost options like index funds or ETFs before venturing into individual stocks or more complex investments.
Step 4: Diversify Your Portfolio, How to Start Investing
- Diversification is key to reducing risk in your investment portfolio. Spread your investments across different asset classes, industries, and geographical regions to minimize the impact of market fluctuations.
Step 5: Monitor and Adjust
- Regularly monitor your investments and make adjustments based on changes in your financial goals or market conditions. Stay informed and be prepared to adapt your investment strategy as needed.
Importance of Research and Due Diligence
Before making any investment decisions, it is crucial to conduct thorough research and due diligence. This includes understanding the investment products, assessing risks, and evaluating potential returns. By taking the time to research and analyze your investment options, you can make informed decisions that align with your financial goals.
Resources and Platforms for Low-Cost Investing
- Robo-advisors: These online platforms offer automated investment solutions at low costs, making it easy for beginners to start investing.
- Discount brokerages: Many brokerage firms provide low-cost trading options and educational resources for new investors.
- Online investment platforms: Platforms like Acorns, Robinhood, and Wealthfront offer low-cost investment opportunities with user-friendly interfaces.